Table of Contents
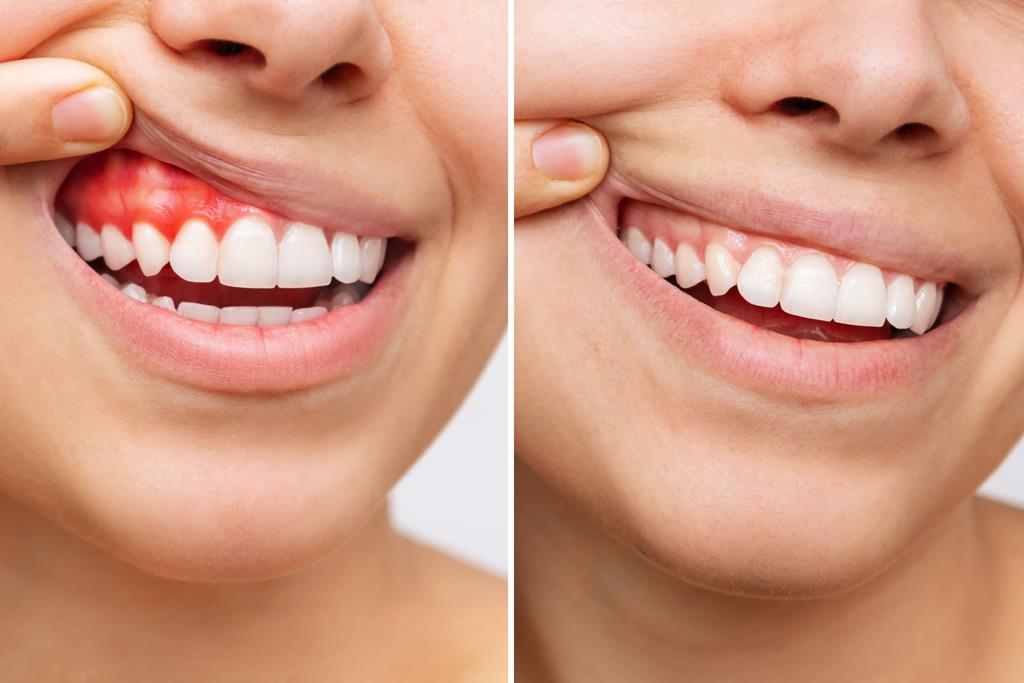
Discover the impact of gum disease on your oral health and learn about the benefits of seeking treatment in Turkey. Synergy Health Travel offers expert care and invites you to experience the top-quality healthcare services while enjoying a memorable journey.
Understanding the Importance of Oral Health
Gum health is a significant issue that necessitates attention because oral health is essential to our overall wellbeing. Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common oral condition that affects a sizable portion of the world’s population. To ensure ideal oral health and general wellness, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of gum disease and its effects.
Gum disease refers to a variety of conditions that affect the gums, ligaments, and bone that support the teeth. Gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums, is usually the first sign, and if untreated, it can develop into periodontitis, a more serious condition.
Our gums are an important part of our body because they act as a barrier to protect the teeth and the structures that support them. Healthy gums are essential for maintaining not only a radiant smile but also the stability and longevity of our teeth.
We will explore all facets of gum disease in this article, including its causes, symptoms, effects, diagnosis, and available treatments. We will also discuss the benefits of receiving dental care for gum disease in Turkey, using the knowledge and resources of Synergy Health Travel, a renowned international health travel company based in Turkey.
You will have learned a lot about gum disease and the advantages of Turkey’s health tourism by the end of this article, enabling you to make wise choices regarding your oral health and perhaps even think about taking a memorable trip to Turkey for dental treatments. Let’s set out on this educational journey to learn the importance of gum health and the potential it holds for a radiant and self-assured smile.
You can also check our other articles:
Tooth Extraction in Turkey: A Comprehensive Guide for International Patients in 2023
Smile like never before: Emax Crowns in Turkey 2023
Dental Crowns in Turkey 2023: Price and Benefits
What is Gum Disease?
Periodontal disease, also referred to as gum disease, is a common oral condition that affects the tissues supporting and enveloping the teeth. If left untreated, it is characterised by gum inflammation and infection, which can have serious repercussions.
Stages of Gum Disease
- Gingivitis: This is primarily characterized by inflammation of the gums. It occurs due to the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and gumline. Gingivitis is often marked by redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums, especially during brushing or flossing. Fortunately, at this stage, gum disease is reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional dental care.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress into periodontitis, which is a more advanced stage. In periodontitis, the infection spreads beneath the gumline, causing the gums to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets. These pockets can become infected and lead to the destruction of the underlying bone and connective tissues that support the teeth. As the disease progresses, it can result in tooth loss and serious oral health complications.
Causes of Gum Disease
Plaque accumulation on the teeth and gumline, a sticky film made of bacteria, food particles, and saliva, is the main contributor to gum disease. Plaque can become tartar (calculus) if it is not thoroughly removed by routine brushing and flossing. This causes additional gum irritation and creates an ideal environment for bacterial growth.
Several factors contribute to the development and progression of gum disease, including:
- Poor oral hygiene habits
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause)
- Diabetes and other systemic diseases
- Certain medications that reduce saliva flow
- Poor nutrition and a diet high in sugary foods and drinks
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early detection and timely intervention. The common symptoms and warning signs of gum disease include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gumline or teeth appearing longer
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Formation of deep pockets between the teeth and gums
- Changes in the way your bite fits together
- Changes in the fit of dentures or dental appliances
The early stages may not always be painful or uncomfortable, so regular dental checkups and expert cleanings are crucial for its early detection and treatment.
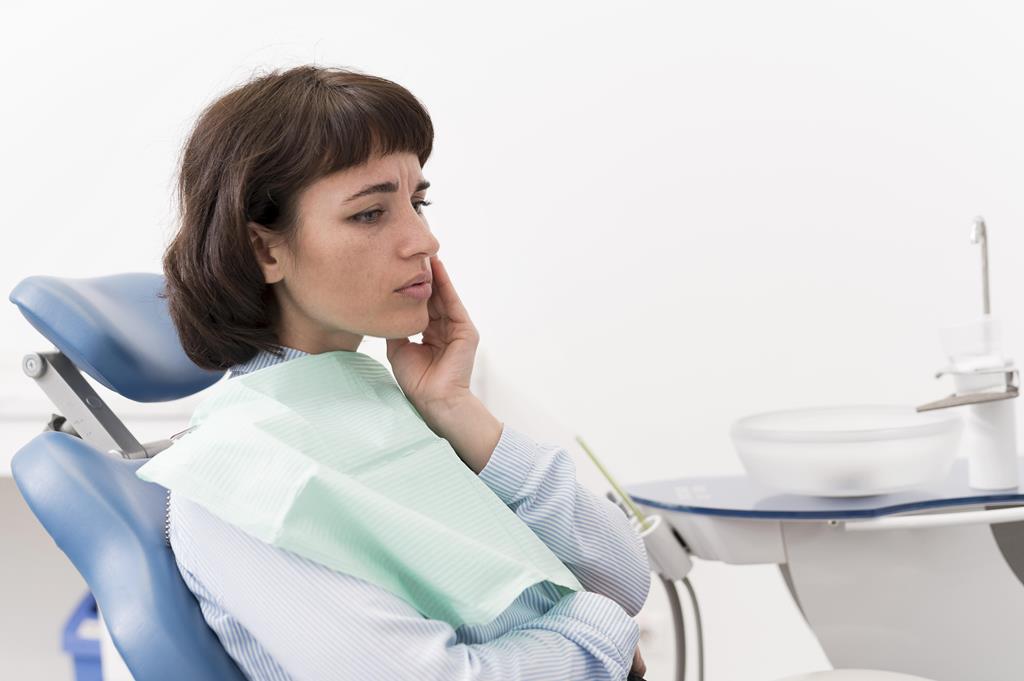

The Consequences of Untreated Gum Disease
Gum disease left untreated can have serious effects on your overall health as well as your oral health. It has effects that go beyond the mouth and may have an effect on different facets of your health. Understanding these repercussions is essential for realising how important it is to seek treatment as soon as possible.
Oral Health Complications
- Tooth Loss: Advanced gum disease can lead to the destruction of the bone and connective tissues that support the teeth. As the condition progresses, teeth may become loose and eventually require extraction.
- Gum Recession: Untreated gum disease can cause the gums to recede, exposing the tooth roots. This can lead to tooth sensitivity, increased vulnerability to decay, and aesthetic concerns.
- Abscesses and Infections: Pockets formed by gum disease can trap bacteria, leading to the formation of abscesses and infections. These can cause pain, swelling, and pus-filled lesions.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath, or halitosis, is a common symptom. The odor is often caused by bacteria and their byproducts in the oral cavity.
- Changes in Bite and Chewing Difficulties: As gum disease progresses and teeth become loose, changes in the way your bite fits together can occur. This can result in difficulties while chewing and speaking.
Impact on Overall Health
Gum disease is strongly linked to a number of systemic diseases, according to research. The gum disease-related inflammation and bacteria can spread to other body regions, raising the risk of the following health problems:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, clogged arteries, and stroke. The bacteria from infected gums can enter the bloodstream, causing inflammation in the cardiovascular system.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled gum disease can make it more challenging to control blood sugar levels. The relationship between gum disease and diabetes is bidirectional, with each condition influencing the other.
- Respiratory Infections: The bacteria from infected gums can be inhaled into the lungs, potentially causing or worsening respiratory infections such as pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Pregnancy Complications: Pregnant women with gum disease have a higher risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and preeclampsia. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can make gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Studies suggest a potential link between gum disease and rheumatoid arthritis, as the bacteria associated with gum disease may trigger an autoimmune response leading to joint inflammation.
Diagnosing Gum Disease
To effectively treat gum disease and stop further complications, early detection is essential. Different diagnostic methods are used by dentists to determine whether gum disease is present and how severe it is. This section will examine typical techniques for diagnosing gum disease and place emphasis on the value of early detection.
Dental Examination and Assessment
Your dentist will carefully inspect your gums, teeth, and overall oral health during a dental examination. They will search for indicators of swelling, bleeding, redness, and inflammation. To gauge the size of the pockets between your gums and teeth, your dentist might use a periodontal probe, a tiny instrument. Gum disease may be present if the pockets are deeper.
Other aspects such as plaque accumulation, tartar (calculus) deposits, tooth mobility, and the state of your bite will also be evaluated by your dentist. To get a complete picture of your oral health situation, they will ask you about your medical history and any symptoms you may be feeling.
X-rays and Other Diagnostic Techniques
X-rays are commonly used in diagnosing gum disease. They provide a detailed view of the underlying bone structure and can reveal any bone loss or abnormalities. X-rays help dentists determine the extent and severity of the disease and assist in planning the appropriate treatment.
In some cases, your dentist may recommend additional diagnostic techniques, such as:
- Dental Imaging: Advanced imaging technologies like cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) can provide three-dimensional images of the teeth, gums, and surrounding structures. These images offer a more comprehensive assessment, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Bacterial Testing: Your dentist may collect a sample of plaque or saliva to test for specific bacteria associated with gum disease. Bacterial testing can help identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and guide the treatment approach.
Importance of Early Detection
Early diagnosis of gum disease is essential for effective treatment and halting further oral health damage. When gum disease (gingivitis) is identified in its early stages, it is typically treatable with professional assistance and good oral hygiene habits. Your dentist can spot any early indications of gum disease and start the proper treatment right away with routine dental checkups.
In addition to preserving your oral health, early detection lowers the chance of complications brought on by advanced gum disease. You can prevent tooth loss, involved treatments, and potential effects on your general health by treating gum disease early.
Treating Gum Disease
Gum disease requires appropriate treatment to control the infection, prevent further damage, and restore gum health. The treatment approach depends on the severity of the disease. In this section, we will explore both non-surgical and surgical treatment options.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Gum Disease
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure is often the initial treatment for gum disease. It involves removing plaque and tartar (calculus) from the tooth surfaces, including the root surfaces below the gumline. Scaling and root planing help eliminate bacteria, reduce inflammation, and promote gum healing.
- Antibiotics and Medications: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to control the infection and reduce bacterial growth. Antimicrobial mouth rinses or gels may also be recommended to aid in reducing bacteria and promoting healing.
- Professional Dental Cleanings: Regular dental cleanings by a dental hygienist are essential. Professional cleanings help remove plaque and tartar buildup, preventing the progression of gum disease and maintaining oral health.
Surgical Treatments for Advanced Gum Disease
If gum disease has progressed to an advanced stage or non-surgical treatments have not effectively controlled the infection, surgical interventions may be necessary. Some common surgical treatments include:
- Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery): In this procedure, the gums are lifted, and tartar deposits are removed from the tooth roots. The gums are then repositioned to reduce the pocket depth, making it easier to maintain proper oral hygiene.
- Bone and Tissue Grafts: Advanced gum disease can cause bone loss and gum recession. Bone grafts involve placing synthetic or natural bone material to stimulate the regeneration of lost bone. Tissue grafts involve taking tissue from one area and placing it in areas with gum recession to restore gum volume and coverage.
- Gum Grafts: Gum grafts are performed to address severe gum recession. Tissue is taken from the palate or another donor source and placed over the exposed tooth roots. This helps protect the roots, improve aesthetics, and prevent further gum recession.
These surgical treatments aim to eliminate infection, restore gum health, and prevent further damage to the teeth and supporting structures.
It is important to note that gum disease is a chronic condition that requires ongoing maintenance and diligent oral hygiene practices. Regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and consistent oral care at home are vital in managing gum disease and preventing its recurrence.
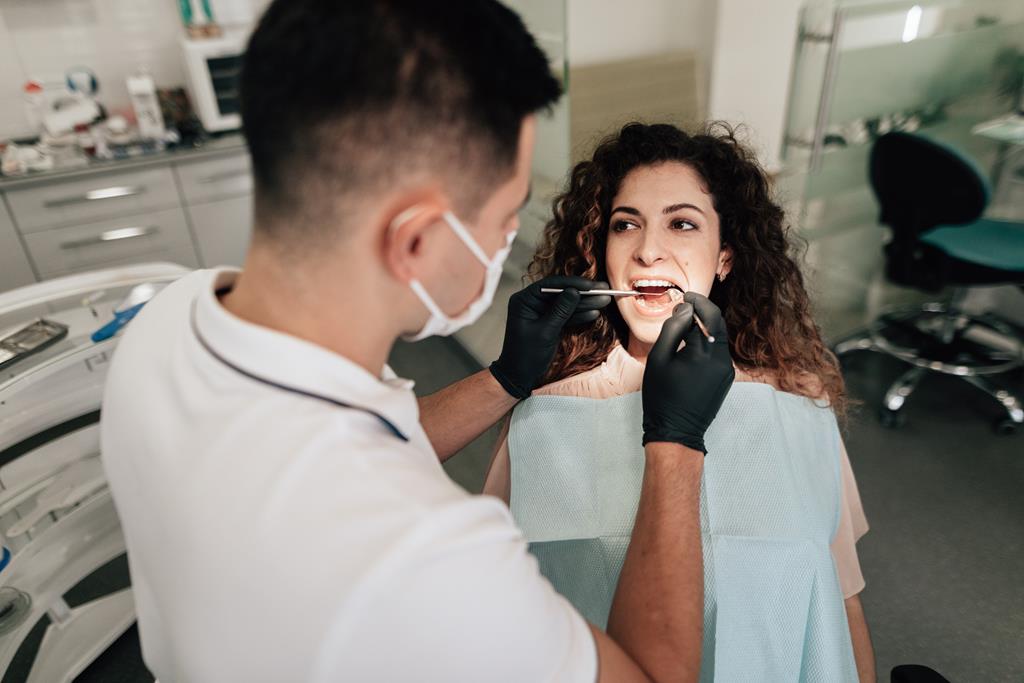
Importance of Timely Intervention
Timely intervention is essential in managing gum disease effectively and preventing its progression. Taking prompt action can help preserve your oral health and prevent further complications. In this section, we will emphasize the importance of early treatment and maintaining good oral hygiene habits to combat gum disease.
Preventing the Progression of Gum Disease
Early intervention is key to preventing gum disease from advancing to more severe stages. When gingivitis, the initial stage is detected, it can be reversed through proper treatment and oral hygiene practices. By addressing gum disease early on, you can avoid the potential consequences associated with advanced stages, such as tooth loss and systemic health implications.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene Habits
Maintaining good oral hygiene habits is crucial in preventing and managing gum disease. Follow these practices to keep your gums healthy:
- Brush your teeth: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Use gentle, circular motions and pay attention to the gumline.
- Floss daily: Clean between your teeth and along the gumline using dental floss or interdental brushes. This helps remove plaque and food particles from areas that a toothbrush may not reach.
- Use mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to help reduce bacteria and freshen your breath. Choose a mouthwash that is specifically formulated for gum health.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks, as they can contribute to the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Avoid tobacco use: Smoking and tobacco use significantly increase the risk of gum disease. Quitting smoking or using tobacco products can improve your gum health and overall well-being.
Regular Dental Check-ups and Cleanings
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are crucial in the early detection and management of gum disease. Your dentist can assess the health of your gums, detect any signs of gum disease, and provide appropriate treatment. Professional cleanings help remove plaque and tartar buildup, which are major contributors to gum disease.
By scheduling regular dental visits, you can stay proactive in maintaining your oral health, receive timely interventions, and receive guidance on effective oral hygiene practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are answers to some commonly asked questions about seeking dental treatment for gum disease in Turkey, through Synergy Health Travel:
1. What is the cost of dental treatments in Turkey compared to other countries?
Dental treatments in Turkey generally offer competitive pricing compared to many other countries. The exact cost may vary depending on the specific treatment required and the complexity of your case. Synergy Health Travel can provide you with detailed information regarding the cost of dental treatments in Turkey, helping you make an informed decision.
2. How can I communicate with the dental professionals in Turkey?
Communication with dental professionals in Turkey is convenient and efficient. Many dental clinics in Turkey have multilingual staff who can communicate in English, ensuring effective communication throughout your treatment process. Additionally, Synergy Health Travel can assist you with any language-related concerns and act as a bridge between you and the dental professionals.
3. Is it safe to travel to Turkey for dental treatments?
Yes, Turkey is a safe destination for dental treatments. As one of the major cities in Turkey, Turkey boasts modern healthcare facilities and experienced dental professionals. Synergy Health Travel works with reputable clinics and ensures that all necessary safety protocols are followed to provide a safe and comfortable experience for patients traveling for dental treatments.
4. What documents do I need for dental treatment in Turkey?
To travel to Turkey for dental treatment, you will typically need a valid passport and any required visas, depending on your country of origin. Synergy Health Travel can guide you through the necessary documentation and provide support in arranging your travel itinerary and accommodation.
5. How long should I plan to stay in Turkey for my dental treatment?
The duration of your stay in Turkey will depend on the specific dental treatment you require. For routine dental procedures, such as scaling and root planing, a shorter stay may be sufficient. However, for more complex treatments like gum grafts or flap surgery, a longer stay may be necessary to ensure proper healing and follow-up appointments. The dental professionals in Turkey will assess your individual case and provide you with an estimated treatment timeline.
Synergy Health Travel will assist you in planning your trip, including scheduling appointments and coordinating your stay in Turkey. They will ensure that your dental treatment journey is seamless and convenient.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gum disease is a common oral health condition that can have significant consequences if left untreated. We have explored the definition and stages of gum disease, its causes, symptoms, and the link between gum disease and systemic conditions. The consequences of untreated gum disease extend beyond oral health, impacting overall well-being.
Diagnosing gum disease through dental examinations, X-rays, and other diagnostic techniques is crucial for early detection. Timely intervention is essential in preventing the progression of gum disease and maintaining optimal oral health. We have discussed non-surgical and surgical treatment options, emphasizing the importance of professional dental cleanings, scaling and root planing, antibiotics, and surgical procedures like flap surgery, bone and tissue grafts, and gum grafts.
Taking action to address gum disease promptly is vital, and maintaining good oral hygiene habits and regular dental check-ups are key in preventing its recurrence. The significance of early detection and treatment cannot be overstated.
Furthermore, choosing health tourism in Turkey, Turkey, through Synergy Health Travel offers numerous benefits. Turkey provides competitive pricing for dental treatments, ensuring affordability without compromising quality. Communication with dental professionals in Turkey is convenient, thanks to multilingual staff and the support of Synergy Health Travel. The city is a safe and welcoming destination for individuals seeking dental treatments.
By choosing Synergy Health Travel, you gain access to their expertise and assistance in arranging your dental treatment journey in Turkey. They will guide you through the process, provide personalized support, and ensure a seamless experience. With their help, you can enjoy the benefits of dental treatments in Turkey and achieve a beautiful, healthy smile.
Don’t let gum disease go untreated. Take the first step towards optimal oral health by considering dental treatment in Turkey through Synergy Health Travel. Embark on a journey to a healthier smile and a brighter future.
Feel free to contact us 🙂
Follow us on Instagram: Synergy Global



